The African Clawed Frog (Xenopus laevis) is native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is a freshwater species that is often found in ponds, streams, and other bodies of water. These frogs are adapted to live in a wide range of aquatic environments and are able to tolerate a wide range of temperatures and water conditions. They are sometimes kept as pets or used in scientific research due to their hardiness and ease of care.
Distinctive Features of African Clawed Frog
| Scientific Name | Xenopus laevis |
| Lifespan | Up to 30 years |
| Color | Various shades of brown, olive, or gray |
| Size | Up to 4 inches |
| Health Risk | Medium |
| Tank Size | Minimum 10 gallons for a single frog, larger for multiple frogs |
| Temperature | Up to 80°F |
| Water pH | Up to 7.8 |
| Filtration | Moderate |
| Tankmates | Best kept with same species, avoid small or delicate tankmates |
| Unique Trait | Webbed feet with sharp claws |
| Famous For | Wide distribution and use in scientific research |
| Temperament | Generally calm |
| Maintenance | Low |
| Adaptability | High |
| Behavior with Kids | Generally good, with supervision |
| Behavior | Aquatic, nocturnal, and active |
| Social | Generally solitary |
The African Clawed Frog is a small species of frog, typically reaching only about 3-4 inches in length as an adult. They are typically brown or gray in color, with dark markings on their backs and a lighter underside. As their name suggests, these frogs have sharp, claw-like protrusions on their hind feet, which they use for digging and climbing.
In terms of lifespan, African Clawed Frogs can live for up to 30 years in captivity, although their lifespan in the wild may be shorter due to predation and other factors.
Some other distinctive features of African Clawed Frogs include their long, slender bodies and their powerful hind legs, which they use for swimming and jumping. They also have a unique reproductive system, with the females having external fertilization in which the males deposit their sperm on the eggs as they are laid. This allows the females to lay their eggs in a variety of locations, including on land, in shallow water, or even attached to plants or other objects.
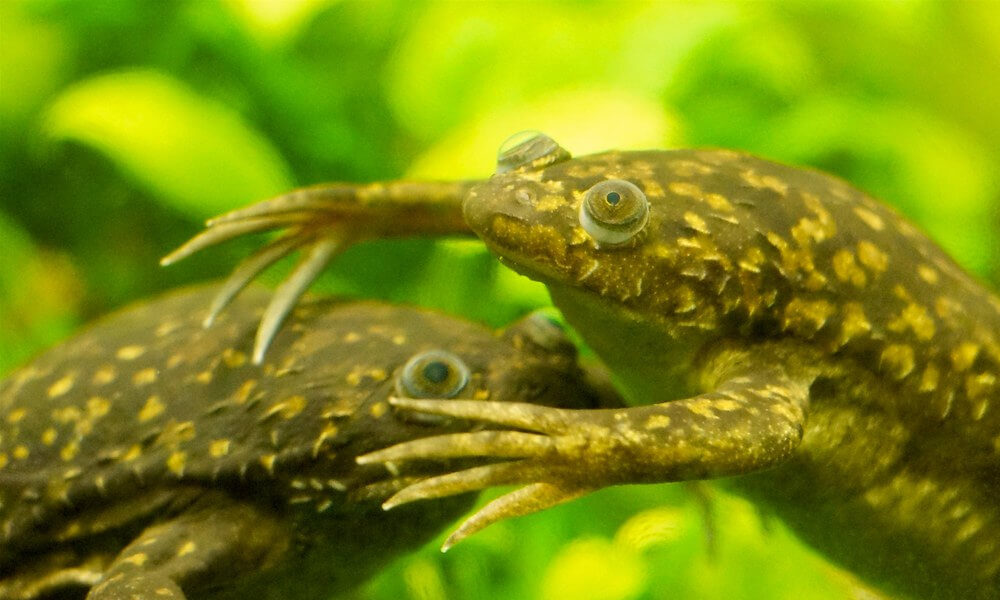
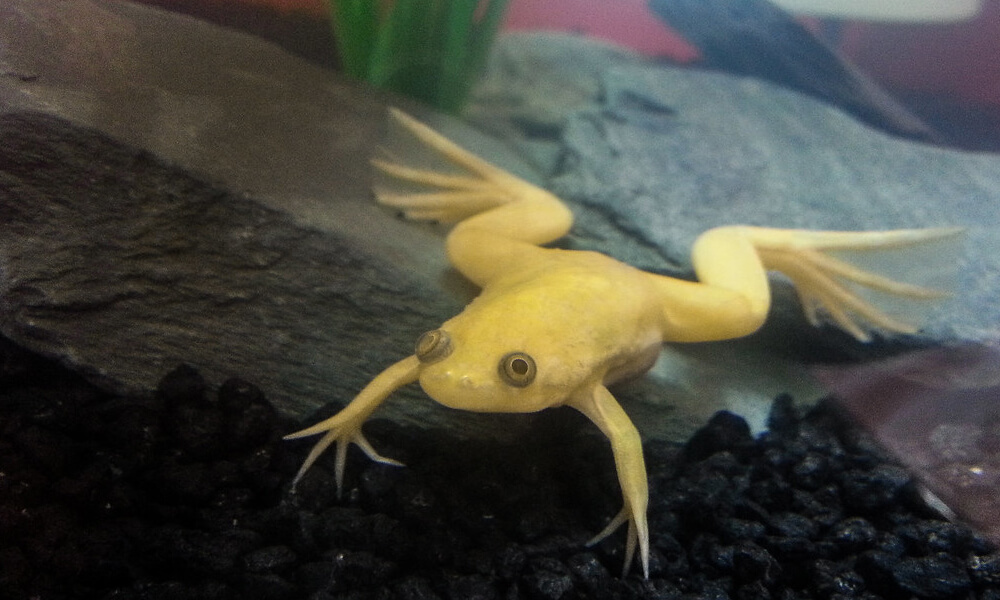


How to Take Care of Pet African Clawed Frog?
When caring for a pet African Clawed Frog, it's essential to create a suitable aquatic environment that mimics their natural habitat. Providing clean water, a balanced diet, and regular monitoring of their health are key aspects of their care.
How to Set Up Habitat for a Pet African Clawed Frog?
If you want to create a habitat for an African Clawed Frog, there are a few key things you will need to consider. First, you will need a suitable enclosure for your frog. This could be a tank or an aquarium, as long as it is large enough (10 gallons at least) for your frog to move around and have some space to itself. You will also need to make sure the enclosure is secure and has a lid, as African clawed frogs are good climbers and can escape if given the opportunity.
Next, you will need to provide the right type of substrate for your frog. African Clawed Frogs are aquatic creatures, so you will need to fill the bottom of the enclosure with water. You can use a mixture of sand and gravel to create a natural-looking substrate for your frog to live on.
You will also need to provide some hiding places and places for your frog to climb and explore. This could be done with rocks, logs, or other types of decorations. Be sure to add enough hiding places so that your frog can feel secure, but not so many that it has difficulty moving around.
Finally, you will need to provide the right lighting and temperature for your frog. African Clawed Frogs are tropical creatures, so they need a warm, humid environment to thrive. You will need to use a heat lamp or other type of heater to maintain a consistent temperature of around 75-80 degrees Fahrenheit. You will also need to provide some form of lighting to simulate the natural day/night cycle, and to provide your frog with the UVB light it needs to maintain healthy skin and bones.
What to Feed Your Pet African Clawed Frog?
African Clawed Frogs are omnivorous, which means they will eat a wide variety of foods. In the wild, they feed on insects, worms, small fish, and other small aquatic creatures. In captivity, they can be fed a diet of commercial frog pellets or fish food, as well as live or frozen foods such as bloodworms, brine shrimp, or earthworms.
Feed your African Clawed Frog a balanced diet to ensure that it stays healthy. You should offer a variety of different foods, including both protein-rich foods and plant-based foods. You can also supplement their diet with occasional treats, such as small pieces of cooked chicken or boiled vegetables.
In terms of feeding frequency, African Clawed Frogs should be fed every day or every other day, depending on their age and size. Juvenile frogs may need to be fed more frequently, while adult frogs can be fed less often. Make sure not to overfeed your frog, as this can lead to health problems such as obesity and organ damage. Instead, offer your frog a small amount of food and remove any uneaten food after a few hours to prevent it from spoiling.
What to Avoid Feeding Your Pet African Clawed Frog?
Feeding your African Clawed Frog the right diet is crucial for its health and well-being. Some foods should be avoided, as they can be harmful to frogs and other animals. For instance, avocados contain persin, which is toxic to frogs. Citrus fruits, like lemons and oranges, are acidic and can upset your frog's stomach. Chocolate contains caffeine and theobromine, both harmful to frogs.
Another food to avoid is raw meat, as it may contain harmful bacteria and organisms that could make your frog sick. Processed foods, like chips and cookies, are not part of a frog's natural diet and can be harmful if consumed in large quantities.
To ensure your African Clawed Frog receives proper nutrition, stick to a diet of commercially prepared frog foods and live or frozen foods like insects, worms, and small aquatic creatures. This balanced diet will provide the necessary nutrients for your frog to stay healthy and thrive. Always monitor your frog's eating habits and consult a veterinarian if you have any concerns about its diet or health.
Health Concerns of African Clawed Frog
African Clawed Frogs, also known as African dwarf frogs, are generally hardy and low-maintenance pets. However, there are a few health concerns that owners should be aware of to ensure the well-being of these aquatic creatures:
- Chytridiomycosis: Chytridiomycosis is a deadly fungal disease affecting African Clawed Frogs, causing skin infections and global population declines. Urgent conservation efforts are needed to protect this vulnerable species.
- Poor Water Quality: African Clawed Frogs are highly sensitive to water quality. Poor water conditions can lead to various health problems, including bacterial or fungal infections, skin irritation, and respiratory issues. Regular water testing and maintenance of proper water parameters, including temperature, pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels, are crucial to prevent water-related health issues.
- Opaque corneas: Opaque corneas can affect the vision of African Clawed Frogs, hindering their ability to see clearly and navigate their environment.
- Loss of hind claws: African Clawed Frogs have lost their hind claws over time, which were once used for gripping and climbing. They now rely on their strong front claws for digging and defense.
- Fluid filled cyst: African Clawed Frogs can develop fluid-filled cysts, which are abnormal sacs containing liquid. These cysts may occur in various parts of their body and require veterinary attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Skeletal deformity: Possible skeletal deformities in African Clawed Frogs include shortened or fused limbs, curved spine, and missing or extra digits, resulting from genetic mutations or environmental factors.
- Aeromonas hydrophila: Aeromonas hydrophila is a bacterium that can cause severe infections in African Clawed Frogs, leading to skin ulcers, lethargy, and potential mortality if left untreated.
- Bloated hind legs: African Clawed Frog experiencing hind leg bloating, possible causes include infection, injury, or metabolic issues. Consult a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Malnutrition: Inadequate or imbalanced diet can result in nutritional deficiencies or obesity in African Clawed Frogs. These frogs are carnivorous and primarily eat live or frozen foods such as bloodworms, brine shrimp, and small insects. Offering a varied and nutritionally balanced diet is essential for their optimal health. Commercially available frog pellets can also be included as part of their diet.
- Skin Problems: African Clawed Frogs have delicate skin that is susceptible to injuries and infections. Skin injuries can occur from rough handling, sharp objects in the tank, or poor water quality. Any cuts, wounds, or discoloration on the skin should be monitored closely, and appropriate treatment, such as using aquarium salt baths or topical antiseptics, may be necessary to prevent infections.
- Parasites: Like other aquatic animals, African Clawed Frogs can be susceptible to various parasites, including external parasites like leeches and internal parasites like worms. Regular observation of the frogs for signs of parasites, such as abnormal behavior, loss of appetite, or visible parasites on the skin, is important. If parasites are suspected, seeking veterinary advice for proper diagnosis and treatment is recommended.
- Obesity: African Clawed Frogs have a voracious appetite and can overeat if given unlimited access to food. Obesity can lead to health issues, such as reduced mobility, organ problems, and a shorter lifespan. Feeding an appropriate amount of food and avoiding overfeeding is crucial in preventing obesity.
- Metabolic Bone Disease (MBD): Insufficient calcium and vitamin D3 in the diet can lead to MBD, a condition characterized by weakened bones, deformities, and difficulty moving. Providing a well-balanced diet and ensuring proper calcium supplementation, either through calcium-rich foods or supplements, is essential to prevent MBD in African Clawed Frogs.
- Impaction: African Clawed Frogs may accidentally ingest substrate or other foreign objects in their tank, leading to impaction. Swallowing indigestible items can cause blockages in the digestive system, leading to serious health issues. Using a substrate that is safe and easy to pass if ingested, such as smooth gravel or bare-bottom tanks, and removing any potential hazardous objects from the tank can help prevent impaction.
Regular observation, proper nutrition, maintaining optimal water conditions, and seeking veterinary care when necessary are key to promoting the health and well-being of African Clawed Frogs.
Other Pets to Keep or Avoid with African Clawed Frog
African Clawed Frogs are generally peaceful and can coexist with other animals in the same enclosure, as long as the other animals are not aggressive or too large to pose a threat. Some examples of animals that can be kept with African Clawed Frogs include:
- Other species of frog: African Clawed Frogs can be kept with other species of frog, as long as the other species is not aggressive, and the enclosure is large enough for both frogs to have their own space.
- Fish: African Clawed Frogs can be kept with small, peaceful species of fish, such as guppies or tetras. However, avoid keeping African Clawed Frogs with larger fish, such as goldfish or cichlids, as these fish may attack or eat the frogs.
- Invertebrates: African Clawed Frogs can be kept with small invertebrates, such as snails or shrimp. These animals can help to keep the enclosure clean and provide a natural source of food for the frogs.
On the other hand, there are some animals that should not be kept with African Clawed Frogs. Some examples of animals to avoid keeping with African Clawed Frogs include:
- Large fish: As mentioned above, African Clawed Frogs should not be kept with large fish, as these fish may attack or eat the frogs.
- Aggressive frog species: African Clawed Frogs should not be kept with aggressive frog species, such as bullfrogs or leopard frogs, as these frogs may attack and harm the African Clawed Frog.
- Mammals: African Clawed Frogs should not be kept with mammals, such as mice or hamsters, as these animals may carry diseases that can be harmful to frogs.
- Reptiles: African Clawed Frogs should not be kept with reptiles, such as snakes or lizards, as these animals may prey on the frogs.
Facts About African Clawed Frogs
There are many interesting facts about African Clawed Frogs. Some of these facts include:
- African Clawed Frogs are native to sub-Saharan Africa, where they are often found in ponds, streams, and other bodies of water.
- African Clawed Frogs are sometimes called "clawed toads" because of the sharp, claw-like protrusions on their hind feet.
- African Clawed Frogs are one of the few species of frog that have external fertilization, with the males depositing their sperm on the eggs as they are laid by the females.
- African Clawed Frogs are often used in scientific research due to their hardiness and ease of care.
- African Clawed Frogs are known for their powerful hind legs, which they use for swimming and jumping. They are also good climbers and can escape from enclosures if given the opportunity.
- African Clawed Frogs are generally peaceful and can coexist with other animals in the same enclosure, as long as the other animals are not aggressive or too large to pose a threat.
What It's Like to Keep African Clawed Frog as a Pet?
Here's what it's like to keep an African Clawed Frog as a pet:
Aquatic Lifestyle: African Clawed Frogs are fully aquatic and spend their entire lives in water. They have a streamlined body shape and powerful hind legs, which allow them to swim gracefully. They are adapted for an aquatic lifestyle with lungs for breathing air and gills for extracting oxygen from water.
Compatibility: African Clawed Frogs are generally peaceful, but they are opportunistic feeders and may eat smaller tankmates, including fish or other frogs. It's best to keep them in a species-only tank or with larger, fast-swimming fish that are not likely to be seen as prey.
Behavior: African Clawed Frogs are mostly active during the night and tend to be more sedentary during the day. They have a curious nature and will often explore their environment and interact with objects in their tank. They have excellent senses, particularly their sense of touch, and use their claws to detect prey or navigate their surroundings.
Handling: African Clawed Frogs have delicate skin that can be easily damaged, so handle them with care. If necessary to handle them, wetting your hands beforehand can help reduce the risk of injuring their skin. However, they are generally not considered a "hands-on" pet, and observation is typically the preferred way to interact with them.
Frequently Asked Questions About African Clawed Frog
Here are answers to some common questions about African Clawed Frogs:
Where is the African Clawed Frog native to?
The African Clawed Frog is native to sub-Saharan Africa, where it is often found in ponds, streams, and other bodies of water.
How long do African Clawed Frogs live?
African Clawed Frogs can live for up to 30 years in captivity, although their lifespan in the wild may be shorter due to predation and other factors.
Can African Clawed Frogs be kept with other animals?
African Clawed Frogs are generally peaceful and can coexist with other animals in the same enclosure, as long as the other animals are not aggressive or too large to pose a threat. Some examples of animals that can be kept with African Clawed Frogs include other species of frog, small fish, and invertebrates.
What is the natural habitat of the African Clawed Frog?
The natural habitat of the African Clawed Frog is sub-Saharan Africa, where they are often found in ponds, streams, and other bodies of water. These frogs are adapted to live in a wide range of aquatic environments and are able to tolerate a wide range of temperatures and water conditions.