Horses were gelded, to begin with by Scythians. They appreciated when gelding made war-horses subdued, reduced mating desire, no calling out to other horses, ease of group living & the chances of fights among the horses decreased.
When a horse is castrated, its testicles the organ that produces the hormone testosterone is removed. However, some male horses are segregated so they stay capable of reproduction. Stallions are meant for mating.
The three types of genders among horses namely:
- Mares- Mares are seldom sprayed because it is a complex surgical method moreover, it is not required. Mares are easy to look after and ride. Owners breed a mare if they so desire.
- Stallions- A stallion is consistently used for breeding. Likely, a winning racehorse career ends early and the chances of its breeding career begin. Stallions are difficult to handle because they possess a healthy breeding instinct. They may fight by kicking, biting, and striking with front legs with other horses for domination. At times it is difficult to hold back a highly charged stallion.
- Gelding- Gelding is a term used for a stallion that is castrated. This is done between the ages of three months to one year. Thus the horse is easy to train, ride, and in the short handle.
What is Castration?
Castration is a surgical process done by a veterinarian for removing the testicles of a male horse. It can be performed by sedation and local anesthesia so the horse does not become distressed. It can be done in a standing position. When general anesthesia is given to the horse it is made to lie on its side. The process is done when the horse is skeletally mature.
A small cut or slit is made in the scrotum and through it, the testes and spermatic cord are removed. The process is not time-consuming and can be accomplished by giving local anesthesia on a standing horse even at home.
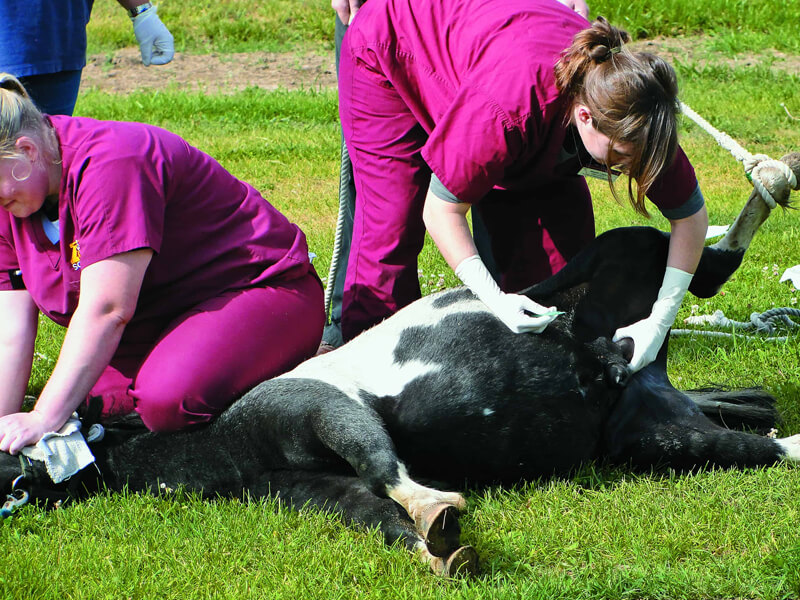

In some horses, the schedule of castration is speeded up because it will have one testicle or maybe both testicles are somewhat undescended. The testicle gets accommodated in the flank of the leg and the abdomen of the horse. Cryptorchid is the term used for a horse that has one testicle normally descended and one undescended. A stallion on which gelding is undertaken later in life maintains stallion-like behavior.
Complications after gelded happen because of poor aftercare. Such a horse should be given the right type and amount of exercise. The incisions should be kept clean until healing takes place. This period of healing is for a couple of weeks. The vets prefer to do gelding in the dryer months of the year.
Older horses are in extra danger from gelding as the blood vessels supplying blood to the testes get accumulated. The vet is the best judge in the matter. However, horses can be gelded at any age. Gelded horse chances of injuring self or other horses get reduced.
What People Are Reading:
What to Know Before Gelding?
To get the horse ready for gelding the horse should be in good health. All immunizations and deworming schedules should be complete. Tetanus injection is a must. Between vaccination and the procedure, there should be a gap of two weeks. Generally, horses are castrated standing in local anesthesia. However, another method is general anesthesia and the procedure is done with the horse lying on the ground. The latest method for cryptorchid testicles procedure is through laparoscopy. In this, the incision is very small. The horse is not traumatized.
What Happens When You Geld a Horse?
Forethought in castrating a horse:
- Maturity-Castrating is done on colts as yearlings that are not destined for breeding.
- Physical well-being- Any disease will endanger the horse when a surgical procedure is done.
- Climatic condition- The incision place remains open so the wound can drain. Monsoon and humid weather are best avoided as the danger of wound contamination increases.
- The place- The procedure is undertaken in a spacious place like a large open grassy area. The safety of the horse and humans is ensured.
- Post-operative care- After surgery it is mandatory to exercise the horse so that swelling around the procedure site gets reduced.
- Occupied horses- If the horse is under work or training it has to break this schedule at least 10 days before surgery.
Why Gelding is Done?
Stallions are driven by testosterone leading to aggression towards other horses and people. As the stallion matures it will be difficult to train it. Research indicates that horses left intact for a long duration 65% will behave according to learned behavior.
Stallion castrated after maturity say six years or older and those who have lived with mares will persist with stallion-like behavior. This includes trying to mount and breed mares. A colt is mostly gelded before it is a year old. This happens when testicles lower into the scrotum. Several owners are of the view that earlier the better so the colt does not learn stallion-like mannerisms.
Gelding removes hormonally driven behavior linked with a stallion. The male horse becomes composed, behaves better, is harmonious, gentle, and easy to handle in everyday chores.
Frequently Asked Questions
Some frequently asked questions related to gelding are as follows:
Can a Gelded Horse Still Breed?
Non-descended testicles are with decreased fertility or are even sterile. This is so because the inguinal canal makes them impotent as sperms are not produced. In a horse with a high breeding promise, the non-descended testicle may be taken away and the normal testicle will remain. Such horses are called monorchids and are fertile stallions. A double-cryptorchid is a complete stallion that can breed a mare even though sterile.
How Long After Gelding are Horses Fertile?
A colt is fertile for a short span say at least two months after being gelded. The mares presence around is a strict no.
Is Gelding Cruel?
A small percentage of horse owners are worried that the gelding procedure will pain the creature or to some extent may reduce its vitality or spirit. However modern techniques cause very little discomfort to the horse. There is very little postoperative displeasure as the horse recovers. Owners choose to geld or not to geld for varying logic but it is not cruel to the animal.