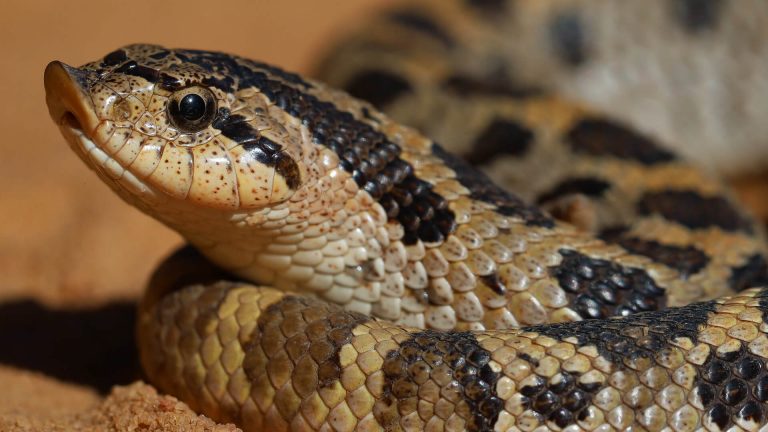
Corn Snakes, popular among reptile enthusiasts, are captivating serpents known for their vibrant colors, docile nature, and relatively easy care requirements. Native to North America, these non-venomous snakes have become a favorite choice for both beginner and experienced snake owners alike. With their distinct patterns and slender bodies, Corn Snakes are a sight to behold.
In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about Corn Snakes, including their diet, behavior, appearance, habitat requirements, and the considerations involved in keeping them as pets. Whether you're considering owning a Corn Snake or simply intrigued by these remarkable reptiles, this guide will provide valuable insights into the world of Corn Snakes and how to provide them with a healthy and fulfilling life in captivity.
Distinctive Features of Corn Snake
| Scientific Name | Pantherophis guttatus |
| Lifespan | Up to 20 years |
| Color | Various colors and patterns |
| Size | Up to 60 inches |
| Health Risk | Low |
| Enclosure Size | 20-30 gallons for adults |
| Temperature Range | 75-85°F (24-29°C) |
| Humidity Range | 40-50% |
| Diet | Carnivorous |
| Unique Trait | Smooth and slender body |
| Famous For | Popular pet snake |
| Temperament | Generally docile |
| Maintenance | Low |
| Adaptability | High |
| Behavior | Generally good with proper handling |
| Personality | Nocturnal and secretive |
| Social | Solitary |
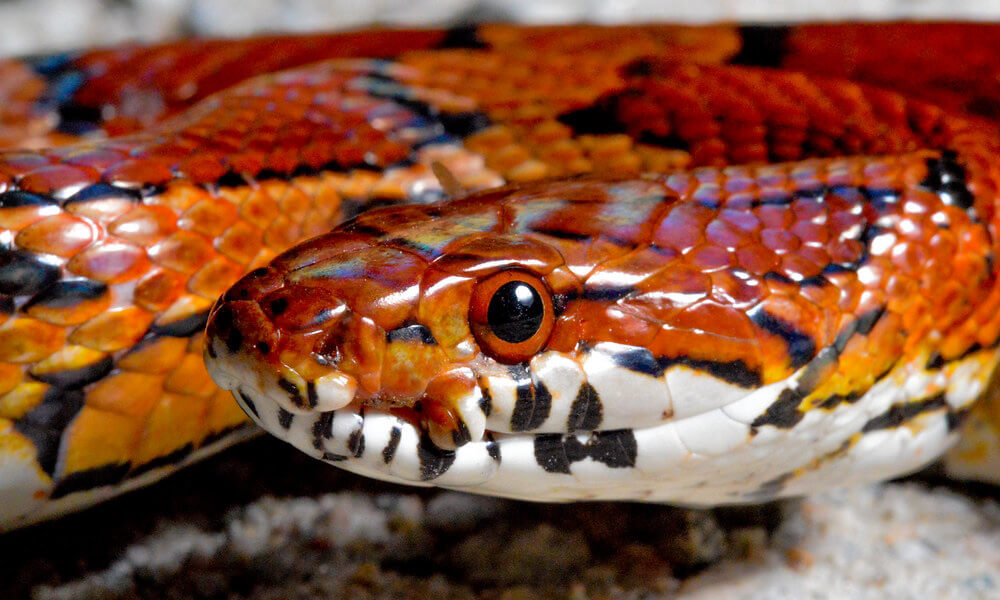
The Corn Snake (Pantherophis guttatus) is a popular and attractive snake species known for its distinctive features. One of its key characteristics is its vibrant and variable coloration, which can include patterns of red, orange, brown, black, and white. This beautiful array of colors resembles the pattern of Indian corn, hence the name "Corn Snake." Another distinguishing feature of the Corn Snake is its slender body, which makes it an agile climber. Additionally, this non-venomous snake species has a docile temperament, making it an ideal choice for beginner reptile enthusiasts. As they are relatively easy to care for and have a long lifespan, Corn Snakes have become a popular choice among snake keepers and pet owners alike.


How to Take Care of Pet Corn Snake?
In the wild, Corn Snakes thrive in different environments like grasslands, rocky regions, farmland, and grain stores. Generally, they live on the ground but given a chance they climb as well.
How to Setup Habitat For Pet Corn Snake?
Corn Snakes are typically bred in captivity by breeders. When creating a captive environment for them, mimic their natural habitat as closely as possible. A suitable setup for a Corn Snake is a vivarium or fish tank with a securely fitted lid. The size of the vivarium should be appropriate for the snake's length, allowing it to fully stretch out. The width and height of the enclosure should be roughly one-third of its length. Providing a shallow pool of water for soaking and drinking is necessary, and a thin layer of substrate at the bottom is recommended.
Some owners opt for specially designed plastic vivariums for their Corn Snakes, which come in various sizes. Establish a thermal gradient in the vivarium, with a heat lamp positioned at one end and a cool water source at the other. Corn Snakes are cold-blooded and rely on external heat sources to regulate their body temperature. Heat mats and bulbs can be used to keep the enclosure warm, mimicking the natural basking behavior of snakes in the wild.
Monitoring the temperature inside the enclosure is crucial. The warm end should be maintained at 28-30 degrees Celsius, while the cool end should range between 20-24 degrees Celsius. Using a thermostat to regulate the temperature is highly recommended. Providing a photo-gradient is important, with varying levels of light to shade. Placing a 2-7 percent UV tube near the hot end can also be beneficial. To establish a day and night cycle, provide 12 hours of light followed by 12 hours of darkness. Placing the enclosure near a window can provide natural light, and incorporating climbing branches and mossy elements adds enrichment.
Maintaining humidity levels around 40-50 percent is essential for the snake's overall health and to prevent respiratory issues. If humidity levels become too high, proper ventilation should be ensured. Different substrates such as aspen shavings, available online or in pet shops, can be used. Spot clean soiled areas regularly, as dirty substrates can lead to health problems. Completely replacing the shavings every month is advisable. When feeding the snake, it should be done away from the aspen shavings to prevent accidental ingestion, which can be harmful.
Certain substrates, such as cedar, redwood shavings, soil, sand, pine shavings, and corncob, should be avoided as they can be toxic or pose ingestion risks. Kitchen rolls or newspapers can be spread on the bottom of the enclosure as a cost-effective and easy-to-replace alternative. It's crucial to ensure a secure lid for the tank, as Corn Snakes are known to push with their nose. Even tiny openings should be prevented, and a mesh lid is ideal for both security and ventilation.
Decorating the snake's enclosure with branches, rocks, plastic plants, terracotta pots, and bark provides a visually appealing and enriching environment. These elements allow the snake to climb, explore, and find hiding places, which is a strong instinctive requirement for them to feel safe. Without a proper hiding place, a Corn Snake may refuse food and experience health issues.
What to Feed Pet Corn Snake?
The Corn Snake is a low-maintenance pet that is relatively easy to care for. When it comes to feeding, young snakes typically require food once a week, while older snakes can be fed every ten to fourteen days. The recommended diet consists of defrosted pre-killed rodents, such as mice. As the snake grows, the size of the mice can be increased from newborn to jumbo mice.
Avoid handling the snake immediately after feeding to prevent regurgitation. Providing accessible drinking water is essential, and using a solid bowl is recommended to prevent snakes from defecating in their water. Keep the water bowl clean. Additionally, some snakes enjoy bathing in water as they prepare to shed their skin.
What to Avoid Feeding Pet Corn Snake?
To ensure the health and well-being of your pet Corn Snake, be aware of foods to avoid feeding them. Here are some items you should refrain from offering as part of their diet:
- Live prey larger than the snake's head: Avoid feeding your Corn Snake live prey that is too large for them to consume comfortably. Overly large prey can lead to regurgitation or cause digestive issues.
- Venomous or toxic prey: Do not feed your Corn Snake any prey items that are venomous or toxic. This includes venomous snakes, poisonous insects, or any creatures known to have toxic secretions.
- Wild-caught prey: It's best to avoid feeding your Corn Snake prey that has been caught from the wild. Wild-caught prey may carry parasites or diseases that can be harmful to your snake.
- Dairy products: Corn Snakes are unable to digest dairy products properly, so it's crucial to avoid offering them any dairy-based foods like cheese or milk.
- Human food: While Corn Snakes may be curious about human food, resist the temptation to feed them table scraps or processed human foods. These items are not suitable for their dietary needs and can lead to digestive issues.
- Toxic plants: Keep your Corn Snake away from any toxic plants or foliage, as ingestion can be harmful or fatal. Research and ensure that any plants present in the snake's enclosure are safe for reptiles.
- Insecticides and pesticides: Any prey items that have been exposed to insecticides or pesticides should not be fed to your Corn Snake. These chemicals can be toxic and pose a risk to their health.
Shedding of Pet Corn Snake
Corn Snakes, like other reptiles, regularly shed their skin as they grow. Shedding, or ecdysis, is a natural process that allows the snake to replace its old skin with a fresh, larger one. Here's some information about shedding in Corn Snakes:
Frequency: Younger Corn Snakes tend to shed more frequently than adults because they grow at a faster rate. Hatchlings may shed every 4-6 weeks, while adults may shed every 6-10 weeks. However, these intervals can vary depending on factors such as the snake's age, health, and environmental conditions.
Signs of Shedding: Before shedding, you may notice some signs that indicate your Corn Snake is about to shed. These signs include a dull or faded appearance of the skin, cloudy or bluish eyes (known as "pre-shed" or "opaque" eyes), reduced appetite, and increased hiding behavior.
Shedding Process: The shedding process usually begins with the snake's skin turning dull and grayish. This is followed by the formation of a fluid-filled layer between the old and new skin. As the new skin develops, the snake's eyes become clear again, indicating that shedding is imminent. The snake will then start rubbing its head against objects in its enclosure to help loosen the old skin around the mouth. It may also use rough surfaces, such as branches or rocks, to aid in the shedding process.
Once the old skin is loosened, the snake will crawl out of it, starting from the head and working its way backward. The entire shedding process may take a few hours to a few days.
Assisting Shedding: Most of the time, Corn Snakes shed their skin without any issues. However, there are a few things you can do to help facilitate a smooth shed. Providing a humid hide box within the enclosure is beneficial, as it creates a more humid microenvironment that aids in the shedding process. This can be achieved by placing a damp substrate (such as sphagnum moss or paper towels) inside a hide box. The increased humidity helps to soften the old skin and make it easier to remove. Ensure that your snake has access to fresh water at all times, as hydration is essential during shedding.
Post-Shed Care: After shedding, your Corn Snake will have a vibrant and fresh-looking skin. However, the newly shed skin may appear slightly dull for a short period until it hardens and gains its natural luster. Be sure to remove and discard the shed skin from the enclosure to maintain cleanliness.
If your Corn Snake has difficulty shedding or experiences retained shed (where some skin remains stuck), address the issue promptly. Increased humidity, gentle misting, or a warm soak can help soften the remaining skin and aid in its removal. If the problem persists or the snake shows signs of distress, it's recommended to consult a reptile veterinarian for further guidance.
Knowing the Health Issues of Pet Corn Snake
Corn Snakes are susceptible to various health issues, including parasitic infections. It is advisable to have the snake tested for parasites before bringing it home. If you notice signs of illness such as listlessness or abnormal vomiting and feces, it is crucial to seek veterinary assistance for proper testing and diagnosis. Mouth rot, also known as infectious stomatitis, is a common infection that can cause tooth loss, saliva, and inflammation around the mouth. Corn Snakes are also prone to fuzngal and respiratory infections, which may manifest as mouth breathing. Consulting a veterinarian is essential for appropriate treatment.
When selecting a Corn Snake as a pet, it is recommended to choose one that is captive-born. Captive-bred snakes are generally healthier and acclimated to captivity. When evaluating a potential pet Corn Snake, look for the following characteristics:
- No remaining shed skin, indicating a healthy shedding process.
- Clear eyes, free from any cloudiness or discharge.
- Absence of cuts, wounds, or scrapes on the skin.
- No presence of mites or ticks, which can be a sign of poor health or improper care.
- Active behavior with a flicking tongue, indicating a responsive and alert snake.
What it's Like to Keep Corn Snake as a Pet?
Here's what it's like to keep a Corn Snake as a pet:
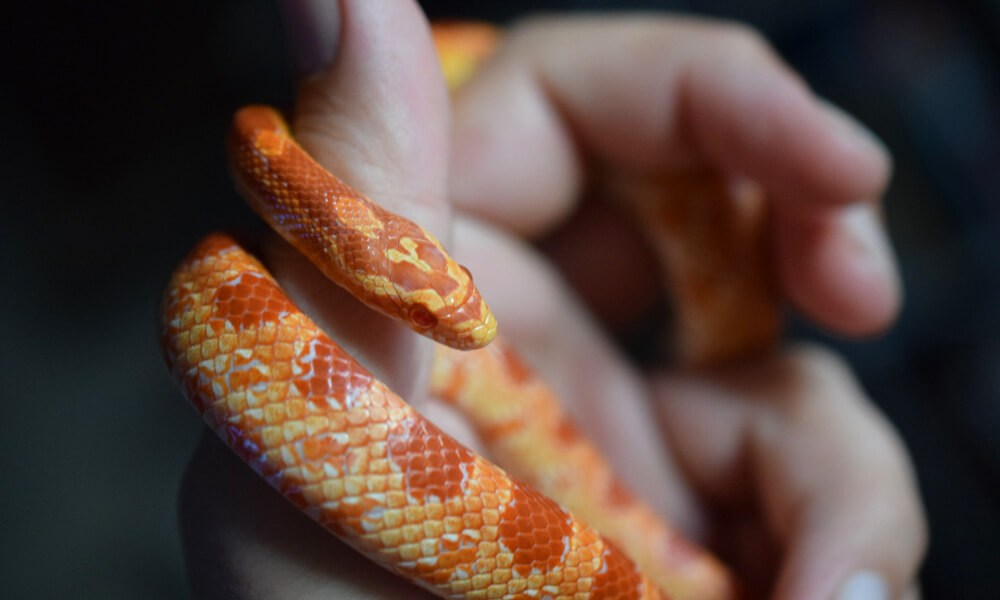
Temperament: Corn Snakes are known for their gentle and docile nature, which makes them popular pets. They are generally tolerant of handling and rarely exhibit aggressive behavior. While individual personalities may vary, most Corn Snakes become accustomed to regular handling and can be easily socialized.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance of the enclosure is necessary to ensure the snake's well-being. This includes spot cleaning of waste, removing shed skin, and providing fresh water at all times. Corn Snakes shed their skin in one piece periodically as they grow, and providing a humid hide box can aid in the shedding process.
Handling: Corn Snakes are known for their docile nature and are generally comfortable with gentle handling. Approach them calmly and support their body when handling. Avoid handling them right after they've eaten, as this can cause stress or regurgitation. As with any snake, regular and consistent handling is essential to maintaining their tolerance and comfort with human interaction.
What People Are Reading:
Frequently Asked Questions About Pet Corn Snake
Some of the commonly asked questions about pet Corn Snakes are answered below:
Are Corn Snakes friendly?
Yes, Corn Snakes are generally considered to be friendly and docile. With proper handling and care, they can become accustomed to human interaction and can be easily handled. However, remember that individual snakes may have different temperaments, so some Corn Snakes may be more shy or skittish than others. It's always recommended to handle any snake with care and respect to ensure both your safety and the well-being of the snake.
Can a Corn Snake hurt you?
While Corn Snakes are not venomous and pose no significant danger to humans, it is still possible for them to bite if they feel threatened or stressed. A bite from a Corn Snake is usually harmless and non-aggressive, often resulting in minor scratches or puncture wounds. Proper handling techniques and gentle interaction can help minimize the chances of being bitten. If you're unsure about handling a snake or if you have concerns, it's always best to seek guidance from an experienced reptile owner or a herpetologist.
How long do Corn Snakes live as pets?
Corn Snakes have a relatively long lifespan compared to some other snake species. With proper care and a suitable environment, Corn Snakes can live for around 15 to 20 years or even longer in captivity.