The Hognose Snake is a harmless native North American snake that has been known to play dead when threatened. They are fairly small, typically 8-24 inches in length, and have the ability to flatten their necks and bodies to appear more like an earthworm. They can also puff up their head to look more like the head of a venomous cottonmouth.
There are several different species of Hognose Snakes, which are native to parts of North and Central America. These snakes are known for their distinctive upturned snouts, which they use to burrow in soil and leaf litter in search of food. Some of the most common species of Hognose Snakes include:
- Western Hognose Snake (Heterodon nasicus): This species is native to the western United States and parts of Canada, and it is known for its distinctive upturned snout and flattened head. Western Hognose Snakes typically grow to be around 2-3 feet in length, although some individuals may reach lengths of up to 4 feet.
- Eastern Hognose Snake (Heterodon platirhinos): This species is native to the eastern United States and parts of Canada, and it is similar in appearance to the western Hognose Snake. Eastern Hognose Snake are typically smaller than western hognose snakes, with an average length of around 2-3 feet.
- Southern Hognose Snake (Heterodon simus): This species is native to parts of Central and South America, and it is known for its distinctive pattern of dark blotches on a light-colored background. Southern Hognose Snakes are typically smaller than the other two species, with an average length of around 1-2 feet.
- Spotted or Mexican Hognose Snake (Heterodon kennerlyi): This species is native to parts of Mexico and Central America, and it is known for its distinctive pattern of dark spots on a light-colored background. Spotted Hognose Snakes are typically smaller than the other species, with an average length of around 1-2 feet.
Distinctive Features of Hognose Snake
| Scientific name | Heterodon spp. |
| Lifespan | Up to 20 years |
| Color | Varies by species; may be solid, patterned, or mottled |
| Size | Up to 48 inches |
| Weight | Varies by size |
| Unique trait | Upturned snout used for burrowing |
| Famous for | "Playing dead" behavior when threatened |
| Temperament | Generally docile and non-aggressive |
| Maintenance | Moderate |
| Adaptability | High |
| Behavior | Generally non-aggressive and safe to handle with supervision |
| Personality | Generally docile and non-aggressive, but may hiss or "play dead" when threatened |
| Social | Generally solitary animals, but may tolerate the presence of other Hognose Snakes |
Hognose Snake is solitary; they rummage and laze in the sunlight early and late in the day. At night they burrow in the loose soil. The western hognose is comparatively tiny and stout-bodied. Between the subspecies, their color and pattern are very variable. The colors are Yellow, Gray, Brown, Olive, Orange, Reddish-brown, Dark brown, Black & Dark Gray.
There are random blotches on the back and smaller blotches on the sides. Some of the snakes are without blotches. The belly color is yellow or light gray or pink. The underside of the tail is lighter compared to the remaining body. Dark lines are drawn from the upper jaw to the eyes. There are 23-25 downwards pointing scales in rows at the mid-body. Pupils are round.
The males are significantly smaller compared to females. They seldom surpass a total length of 15-20 inches. Copulation happens in early February and March. The males generally follow the females for many days before copulation. The oviparous species where the female lays 4-23 elongated 1.25 inches, whitish refined-shelled leathery eggs by June-August. Eggs are amassed in moist sandy, hollow holes or under debris. The eggs are hatched in 60 days. The hatchling is 5-9 inches in length. It takes two years for it to reach sexual maturity.
The life expectancy is up to 20 years. Birds of prey and other snakes eat hognose. Several predators are fooled by the self-defense technique of playing dead. These snakes are also called puff adders. When faced with a threatening situation they puff up the skin of their neck and raise their head off the ground. They even hiss and lunge toward the attacker. If these tactics fail they turn over and play dead.
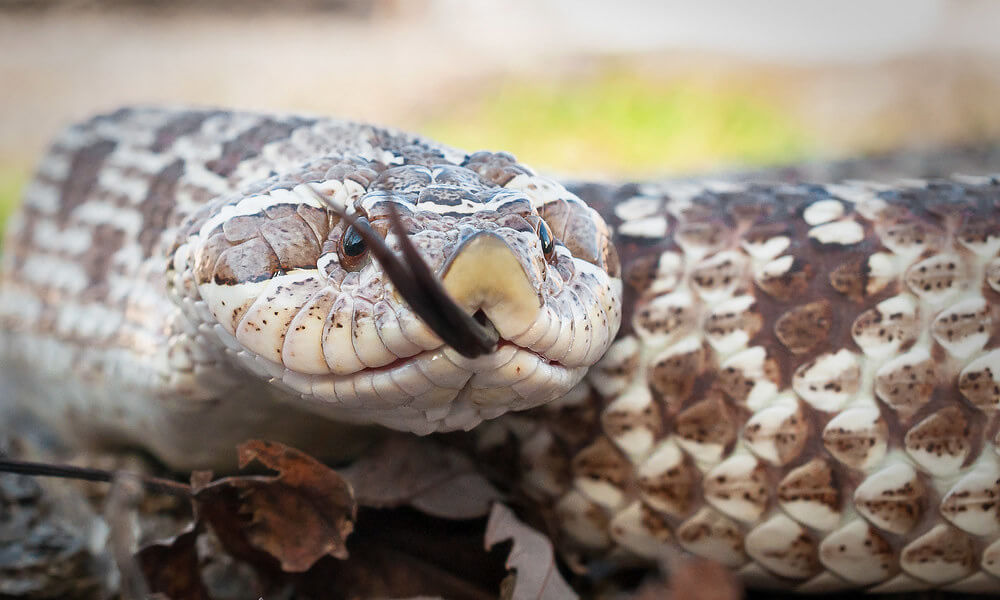


How to Take Care of Pet Hognose Snake?
The Hognose Snake is harmless and docile. It's also not an aggressive animal, which means that it won't cause any harm if you aren't an aggressor too. Hognose Snakes are easy to handle and for this reason, they are the perfect choice for a pet. When kept as a pet, one should know what to feed and how to set up their perfect habitat to make them live longer.
How to Setup Habitat for Pet Hognose Snake?
The snake is not big even at maximum growth. Purchase a tank that permits them to elongate. For a single snake, a 20-gallon tank will suffice. Prearrange floor space rather than height. Mostly these snakes do not climb. Cover the top with a lid for the safety of the creature. The water dish should be big enough to accommodate the snake. A hide box will make it feel secure.
- Temperature: The basking region should be about 85-90 degrees F. The cool region should not go below 70 degrees F. To get this set up take a trial of different wattages of heat bulbs varying their height to get the set goal. Measure the temperature where the snake rests and not of the top layer.
- Brightness: To achieve day-night light you can use full-spectrum UVB lights for a 12-hour cycle. The snakes get Vitamin D from their diet. The light will help in the production of vitamin D.
- Humidity: The humidity requirement of the snake rests at 30%-60%. The need is higher when they shed. The water dish can be a source of humidity and it can be supplemented by a light mist. Keep a check through the reptile hygrometer.
- Substrate: Have the foundation with some inches of sand mix and reptile-safe soil. The snake will burrow and hide.
What to Feed Pet Hognose Snake?
In the wild, the adult and young snake eats mostly amphibians like big and small frogs, toads as well as small lizards. Sometimes they eat rodents. They also eat invertebrates, reptiles, small snakes, and insects.
This snake is problematic to feed in captivity as it will likely deny food. Consistent temperature of the enclosure and feeding time is the ready answer. Warmth keeps the snake active and food gets digested. When hungry the snake accesses the feeder with an open mouth.
In captivity, the snake will accept gut-loaded crickets dredged in calcium powder. As they become big they eat pinkies, fuzzies, and adult mice. The young ones require food a few times a week. Adults' diet suffices one prey item a week. When shedding happens to lessen feeds to avoid regurgitation.
What to Avoid Feeding Pet Hognose Snake?
Feeding your pet Hognose Snake a proper diet is essential for its health and well-being. To ensure the best care for your snake, there are certain foods that should be avoided. Here are some items to steer clear of when feeding your pet Hognose Snake:
- Large prey items: Avoid feeding your Hognose Snake prey items that are too large for it to handle comfortably. Offering prey that is too large can lead to digestive issues or even regurgitation. It's important to choose prey items that are appropriately sized for your snake's age and size.
- Venomous or wild-caught prey: Never feed your Hognose Snake venomous snakes or prey that has been caught from the wild. Wild-caught prey can introduce parasites, diseases, or pesticides that may harm your snake. Stick to feeding pre-killed or frozen/thawed prey purchased from reputable sources.
- Live prey that can harm your snake: While some snakes may be able to handle live prey, it is generally recommended to feed pre-killed or frozen/thawed prey to Hognose Snakes. Live prey can potentially injure your snake during feeding, especially if the prey item is too large or aggressive.
- Toxic prey items: Avoid feeding your Hognose Snake prey items that are known to be toxic or have toxic parts. For example, insects like fireflies, centipedes, and certain beetles are toxic to reptiles and should not be offered as food.
- Large quantities of fatty prey: Limit the intake of fatty prey items, such as rodents with excessive fat content. While some fat in the diet is necessary, too much can lead to obesity and health issues. Ensure a varied diet with a proper balance of nutrients.
What are the Health Concerns of Pet Hognose Snake?
For owners, it is a relief to know that hognose is a sturdy breed and does not fall sick very often. Yet, be alert for some possible sicknesses. Vet specializing in reptiles can help.
- Respiratory infection: Wheezing, drooling, and overall lethargy. Lack of proper humidity leads to this problem.
- Mouth rot or infectious stomatitis: Symptoms are saliva bubbles and redness around the mouth. It is a painful condition. In case timely treatment is not given the likelihood of teeth falling is high.
- Fungal infection: Complications in shedding and discoloration of the skin.
What it's Like to Keep Hognose Snake as a Pet?
Here's what it's like to keep a Hognose Snake as a pet:
Temperament: Hognose Snakes are known for their unique behaviors and interesting temperament. While they are generally docile and non-aggressive, they can display defensive behaviors when they feel threatened. This can include hissing, puffing up their bodies, flattening their necks, and even playing dead by rolling onto their backs and opening their mouths. However, they rarely bite and are considered harmless to humans.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance of the enclosure is necessary to keep it clean and hygienic. This includes spot cleaning of waste, removing shed skin, and cleaning the water dish regularly. Hognose Snakes may also require periodic bathing to assist with shedding.
Handling: Hognose Snakes can be handled with care and are generally tolerant of gentle handling. However, allow them time to acclimate to their new environment before attempting to handle them. Always support their body and avoid sudden movements to prevent stress. Some Hognose Snakes may prefer to burrow or hide rather than being handled frequently, so respect their individual preferences.
What People Are Reading:
Frequently Asked Questions About Pet Hognose Snake
Some of the generally asked questions related to pet Hognose Snakes are answered below:
Is Hognose Snake a good pet?
Hognose Snakes are fearful and choose to hide from predators in the wild. In captivity, they never turn hostile or aggressive. They are easy to care for once housing and feeding get into a routine. They are great pets for young and new owners. The size is convenient. They need an enclosure for life once they are adults.
How poisonous is a Hognose Snake?
Hognose Snake is not risky for humans. In medical science, no importance is attached to the venom of this species. No death or allergic reaction has been recorded. Typically these snakes rarely bite. Experts feel they are not on the same level in poison as cobras or rattlesnakes.
What happens if a Hognose Snake bites you?
The Hognose Snake is a placid reptile that only bites when provoked. If it does bite you, don't fret as it rarely causes any harm or pain because they have weak venom and teeth.